Profiling Go Programs里详细举例说明了如何看pprof报告,但并没有清晰简明的告知读者提供数字的是什么意思,所以本文做一个归纳笔记。
解读CPU
以文中提供的CPU Profile来举例说明,我们使用go tool pprof -http=0.0.0.0:4231 havlak1 havalk1.prof来观察
解读Top
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
(pprof) top10
Total: 2525 samples
Flat Flat% Sum% Cum Cum% Name
298 11.8% 11.8% 345 13.7% runtime.mapaccess1_fast64
268 10.6% 22.4% 2124 84.1% main.FindLoops
251 9.9% 32.4% 451 17.9% scanblock
178 7.0% 39.4% 351 13.9% hash_insert
131 5.2% 44.6% 158 6.3% sweepspan
119 4.7% 49.3% 350 13.9% main.DFS
96 3.8% 53.1% 98 3.9% flushptrbuf
95 3.8% 56.9% 95 3.8% runtime.aeshash64
95 3.8% 60.6% 101 4.0% runtime.settype_flush
88 3.5% 64.1% 988 39.1% runtime.mallocgc
|
先了解是如何采样的:
- 采样频率是每秒100次
- 一个样本包含goroutine栈的程序计数器(program counters)
- 每次只会采样调用栈的前100行
原文中没有给出列名,这里给了出来,下面是解释:
- Total:总共采样次数,这里是2525次。
- Flat:函数在样本中处于运行状态的次数。简单来说就是函数出现在栈顶的次数,而函数在栈顶则意味着它在使用CPU。
- Flat%:Flat / Total。
- Sum%:自己以及所有前面的Flat%的累积值。解读方式:表中第3行Sum% 32.4%,意思是前3个函数(运行状态)的计数占了总样本数的32.4%
- Cum:函数在样本中出现的次数。只要这个函数出现在栈中那么就算进去,这个和Flat不同(必须是栈顶才能算进去)。也可以解读为这个函数的调用次数。
- Cum%:Cum / Total
解读图
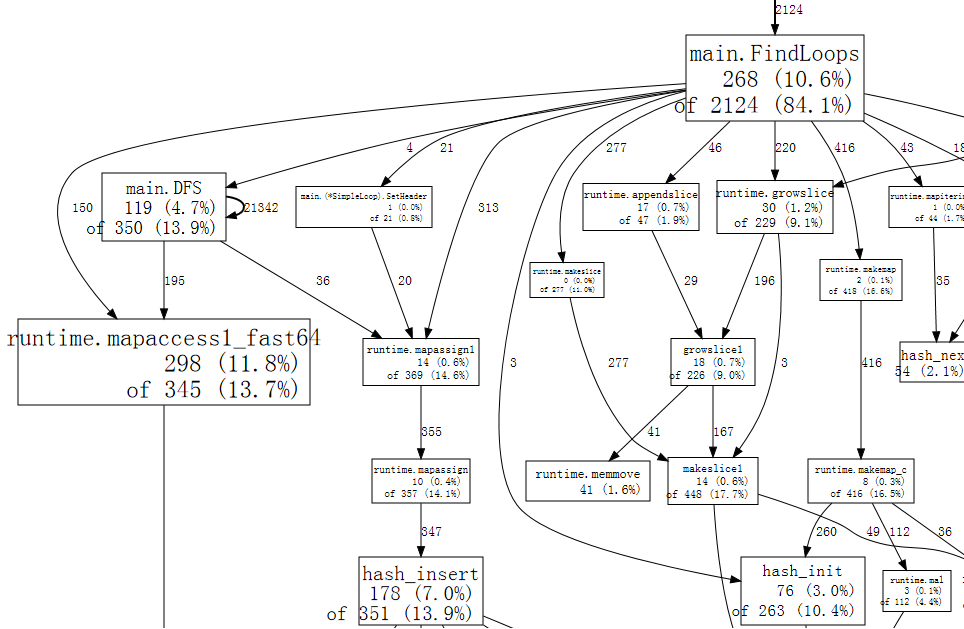
- 方框:函数
- 方框尺寸:代表了Flat的次数
- 箭头:X调用Y
- 线条:记录了X调用Y的次数。数字越大,线条越粗。图中main.DFS有一个指向自己的箭头,说明存在递归调用,而且调用了21342次。
- 方框第一行数字:Flat (Flat%),栈顶次数
- 方框第二行数字:Cum (Cum%),调用次数
解读源码
下面是在pprof交互cli界面看到的报告:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
(pprof) list DFS
Total: 2525 samples
ROUTINE ====================== main.DFS in /home/rsc/g/benchgraffiti/havlak/havlak1.go
119 697 Total samples (flat / cumulative)
3 3 240: func DFS(currentNode *BasicBlock, nodes []*UnionFindNode, number map[*BasicBlock]int, last []int, current int) int {
1 1 241: nodes[current].Init(currentNode, current)
1 37 242: number[currentNode] = current
. . 243:
1 1 244: lastid := current
89 89 245: for _, target := range currentNode.OutEdges {
9 152 246: if number[target] == unvisited {
7 354 247: lastid = DFS(target, nodes, number, last, lastid+1)
. . 248: }
. . 249: }
7 59 250: last[number[currentNode]] = lastid
1 1 251: return lastid
(pprof)
|
下面是在Web界面看到的报告(基本差不多,见这里):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
havlak1
Total: 5758 samples
main.DFS
/home/rsc/g/benchgraffiti/havlak/havlak1.go
Total: 225 2296 (flat / cumulative samples)
235 return false
236 }
237
238 // DFS - Depth-First-Search and node numbering.
239 //
240 3 3 func DFS(currentNode *BasicBlock, nodes []*UnionFindNode, number map[*BasicBlock]int, last []int, current int) int {
241 18 19 nodes[current].Init(currentNode, current)
242 166 number[currentNode] = current
243
244 2 2 lastid := current
245 167 167 for _, target := range currentNode.OutEdges {
246 17 508 if number[target] == unvisited {
247 10 1157 lastid = DFS(target, nodes, number, last, lastid+1)
248 }
249 }
250 7 273 last[number[currentNode]] = lastid
251 1 1 return lastid
252 }
253
254 // FindLoops
255 //
256 // Find loops and build loop forest using Havlak's algorithm, which
|
解读内存
以文中提供的内存Profile来举例说明,我们使用go tool pprof -http=0.0.0.0:4231 havlak3 havalk3.mprof来观察。
pprof提供了4种视角,默认是-inuse_space:
-inuse_space :live object占用内存-inuse_objects :live object的数量-alloc_space :程序启动到现在,总共分配的内存-alloc_objects :程序启动到现在总共object的数量
解读Top
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
(pprof) top5
Total: 82.4 MB
Flat Flat% Sum% Cum Cum% Name
56.3 68.4% 68.4% 56.3 68.4% main.FindLoops
17.6 21.3% 89.7% 17.6 21.3% main.(*CFG).CreateNode
8.0 9.7% 99.4% 25.6 31.0% main.NewBasicBlockEdge
0.5 0.6% 100.0% 0.5 0.6% itab
0.0 0.0% 100.0% 0.5 0.6% fmt.init
(pprof)
|
采样频率:
- 每分配512K,采样一个block(具体啥意思不知道)
照例我们加上列:
- Total:总共占用内存
- Flat:函数分配的内存,不包含它调用其他函数造成的内存分配。
- Flat%:Flat / Total
- Sum%:自己和前面所有的Flat%累积值
- Cum:这个函数分配的内存,以及它调用其他函数分配的内存之和。可以解读为因为这个函数所造成的所有内存分配。
- Cum%:Cum / Total
解读源码
和CPU源码解读差不多:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
(pprof) list FindLoops
Total: 82.4 MB
ROUTINE ====================== main.FindLoops in /home/rsc/g/benchgraffiti/havlak/havlak3.go
56.3 56.3 Total MB (flat / cumulative)
...
1.9 1.9 268: nonBackPreds := make([]map[int]bool, size)
5.8 5.8 269: backPreds := make([][]int, size)
. . 270:
1.9 1.9 271: number := make([]int, size)
1.9 1.9 272: header := make([]int, size, size)
1.9 1.9 273: types := make([]int, size, size)
1.9 1.9 274: last := make([]int, size, size)
1.9 1.9 275: nodes := make([]*UnionFindNode, size, size)
. . 276:
. . 277: for i := 0; i < size; i++ {
9.5 9.5 278: nodes[i] = new(UnionFindNode)
. . 279: }
...
. . 286: for i, bb := range cfgraph.Blocks {
. . 287: number[bb.Name] = unvisited
29.5 29.5 288: nonBackPreds[i] = make(map[int]bool)
. . 289: }
...
|
可以发现L288占用了29.5M内存。用-inuse_objects来观察,可以看到分配次数:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
$ go tool pprof --inuse_objects havlak3 havlak3.mprof
Adjusting heap profiles for 1-in-524288 sampling rate
Welcome to pprof! For help, type 'help'.
(pprof) list FindLoops
Total: 1763108 objects
ROUTINE ====================== main.FindLoops in /home/rsc/g/benchgraffiti/havlak/havlak3.go
720903 720903 Total objects (flat / cumulative)
...
. . 277: for i := 0; i < size; i++ {
311296 311296 278: nodes[i] = new(UnionFindNode)
. . 279: }
. . 280:
. . 281: // Step a:
. . 282: // - initialize all nodes as unvisited.
. . 283: // - depth-first traversal and numbering.
. . 284: // - unreached BB's are marked as dead.
. . 285: //
. . 286: for i, bb := range cfgraph.Blocks {
. . 287: number[bb.Name] = unvisited
409600 409600 288: nonBackPreds[i] = make(map[int]bool)
. . 289: }
...
(pprof)
|
分析GC
你可以通过CPU Profile来分析GC:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
(pprof) top10
Total: 1173 samples
205 17.5% 17.5% 1083 92.3% main.FindLoops
138 11.8% 29.2% 215 18.3% scanblock
88 7.5% 36.7% 96 8.2% sweepspan
76 6.5% 43.2% 597 50.9% runtime.mallocgc
75 6.4% 49.6% 78 6.6% runtime.settype_flush
74 6.3% 55.9% 75 6.4% flushptrbuf
64 5.5% 61.4% 64 5.5% runtime.memmove
63 5.4% 66.8% 524 44.7% runtime.growslice
51 4.3% 71.1% 51 4.3% main.DFS
50 4.3% 75.4% 146 12.4% runtime.MCache_Alloc
(pprof)
|
可以看到runtime.mallocgc的调用次数占了50.9%。
查看系统为何进行垃圾收集的另一种方法是查看导致收集的分配,这些分配在mallocgc中花费了大部分时间。使用--nodefraction=0.1去掉占比小于10%的结果:
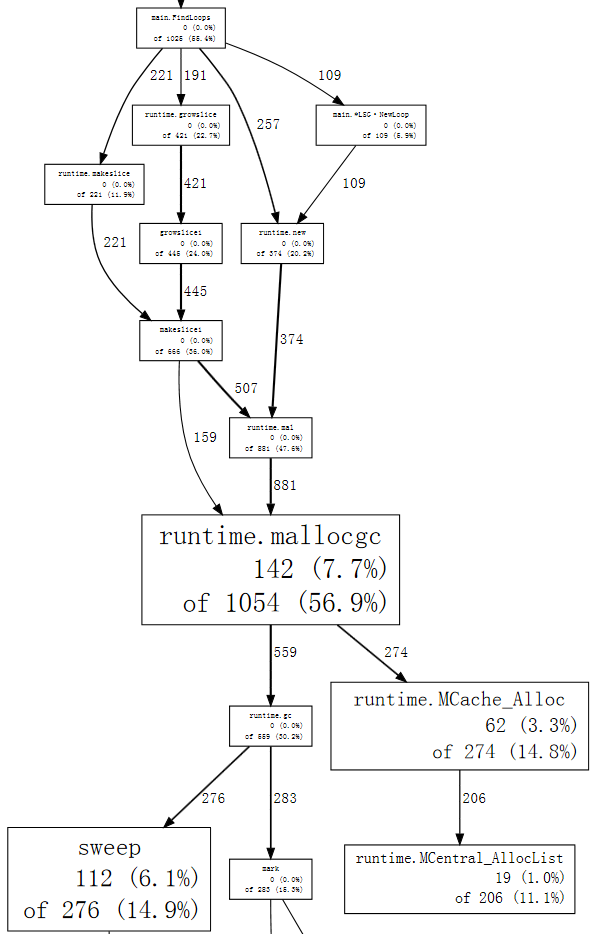
可以看到main.FindLoops导致了大多数GC。
在线Profile
如果你是一个Web应用,你可以使用net/http/pprof来添加一个Handler,访问http://<host>:<port>/debug/pprof/可以得到功能列表:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
/debug/pprof/
Types of profiles available:
Count Profile
8 allocs
0 block
0 cmdline
10 goroutine
8 heap
0 mutex
0 profile
19 threadcreate
0 trace
...
|
然后你可以通过这样来用go tool pprof <url>来分析,比如:
1
2
3
4
|
# 分析CPU
go tool pprof http://localhost:9090/debug/pprof/profile
# 打开网页分析heap
go tool pprof -http=0.0.0.0:4231 http://localhost:9090/debug/pprof/heap
|
在生产中,你需要对/debug/pprof/*做HTTP BasicAuth保护(很简单,一个响应头和请求头罢了),那么你去抓取数据分析的时候得这样:
1
|
go tool pprof http://<user>:<password>@localhost:9090/debug/pprof/profile
|
参考资料


评论