Check Subtree: T1 and T2 are two very large binary trees, with T1 much bigger than T2. Create an algorithm to determine if T2 is a subtree of T1.
A tree T2 is a subtree of T1 if there exists a node n in T1 such that the subtree of n is identical to T2. That is, if you cut off the tree at node n, the two trees would be identical.
Hints:#4, #11, #18, #31, #37
解法
看这个题目意思好像是,不能说T2的root node出现在T1中就能认定T2是T1的子树。而是说两棵树看上去一模一样。
第一个想到的如果T2是T1的子树,那么是不是说T2的遍历字符串是T1遍历字符串的子串?
看下面这张图(图中的X代表NULL,如果没有这个的话即使遍历字符串一样也不代表两颗树就一样):
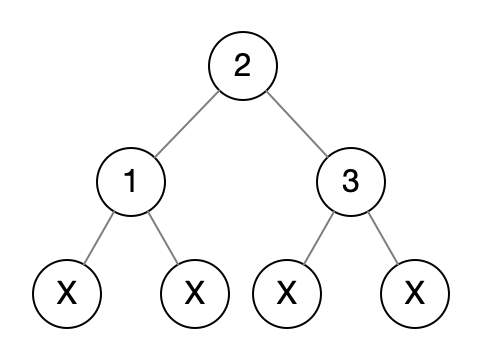
它的前、中、后序遍历结果是:
|
|
其中中序遍历结果不能唯一的用来标示一颗树,看下面这张图的:
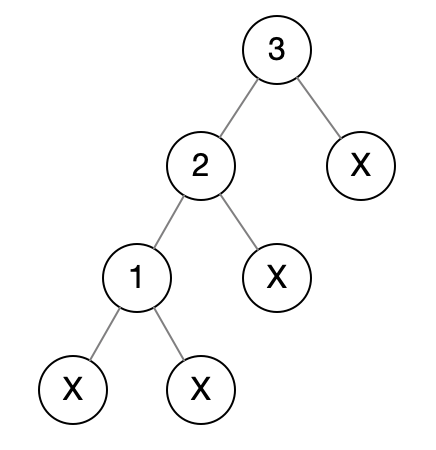
它的前、中、后序遍历结果是:
|
|
可以发现中序遍历结果是一样的,这是为什么呢?因为中序遍历一般都用在BST中,用它来得到从小到大都有序数组。中序遍历本身只表达了大小关系,并没有办法表达结构关系。
可以使用前序、后序遍历来判断T2是否T1的子树。这里用前序:
|
|
时间复杂度:O(m + n),m是T1节点数量,n是T2节点数量
空间复杂度:O(m + n)
解法2
解法1空间复杂度比较高,希望能够节省空间。
解法2采用的方式是,在T1中找到匹配T2根的节点,然后从这个节点开始判断其子树是否和T2相等。
|
|
时间复杂度:O(m + k * n),m是T1节点数量,n是T2节点数量,k是T1中data==T2根data的节点数量
空间复杂度:O(1)
如果节点里都是数字,取值范围是 [0, p],那么T1中data==T2根data的节点数量概率是多少?答案是m/p。
因为T2根data的概率是1/p,而T1有m个节点,那么概率就是m/p。
假设p=10,000,m=100,000,n=100,那么时间复杂度则是 O(100,000 + 100,000 / 10,000 * 100)=O(101,000)。
而且k * n中的n不是每次都会用足的,当在检查过程中发现节点不对的话就会中断掉的。
最坏情况是 O(m + m * n) 也就是 T1中的每个节点都和T2根节点匹配。不过这个是不太可能的。
补充思考:这个方法用到了递归,如果T1有大量节点,那么递归层次会很深,可以采用BFS(广度优先)的方法来做。
评论